Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment
Neuropathy Treatment
A revolutionary pain management system we offer is called Electroanalgesia (EA). This system is one of the most effective non-surgical, drug-free treatments available. While pain medications can temporarily relieve pain, they may also produce undesirable side effects or even result in dependence. This device delivers precise dosages of electrical stimulation to peripheral nerves (the nerves that connect the brain and spinal cord to limbs and organs).
If you have ever had physical therapy, you may be familiar with TENS (Transcutaneous Electric Nerve Stimulation), an external device that reduces pain by applying low voltage electricity through electrodes placed over the skin. Similar in concept to TENS, electroanalgesic treatments also use electrical frequencies to decrease pain, although at rates much higher than those delivered by TENS. For example, TENS units deliver 1 to 250 pulses per second, while Electroanaglesia (EA) delivers 8,300 to 10,000 pulses per second.
Due to lowered skin resistance, this electrical energy is delivered deeper into the patient’s tissue. Rather than stimulate the nerves, higher frequencies reduce the ability of the affected nerves to transmit pain signals and, at the same time, promote healing. It’s like a block with electricity instead of an injection (such as an epidural). With the correct dosage and electrodes, Electroanaglesia can safely and effectively decrease pain intensity, providing patients with an improved quality of life.
We are proud to offer the only Electroanaglesia machine in Northern California and we are highly skilled in administering this treatment.
Causes
Peripheral neuropathy is nerve damage caused by several conditions. Causes of neuropathies include:
- Alcoholism. Poor dietary choices made by people with alcoholism can lead to vitamin deficiencies.
- Autoimmune diseases. These include Sjogren's syndrome, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, Guillain-Barre syndrome, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, and necrotizing vasculitis.
- Diabetes. More than half the people with diabetes develop some type of neuropathy.
- Exposure to poisons. Toxic substances include heavy metals or chemicals.
- Medications. Certain medications, especially those used to treat cancer (chemotherapy), can cause peripheral neuropathy.
- Infections. These include certain viral or bacterial infections, including Lyme disease, shingles, Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis C, leprosy, diphtheria, and HIV.
- Inherited disorders. Disorders such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease are hereditary types of neuropathy.
- Trauma or pressure on the nerve. Traumas, such as from motor vehicle accidents, falls or sports injuries, can sever or damage peripheral nerves. Nerve pressure can result from having a cast or using crutches or repeating a motion such as typing many times.
- Tumors. Growths, cancerous (malignant) and noncancerous (benign), can develop on the nerves or press nerves. Also, polyneuropathy can arise as a result of some cancers related to the body's immune response. These are a form of paraneoplastic syndrome.
- Vitamin deficiencies. B vitamins including B-1, B-6 and B-12 as well as vitamin E and niacin (B3) are crucial to good nerve health.
- Bone marrow disorders. These include abnormal protein in the blood (monoclonal gammopathies), a form of bone cancer (osteosclerotic myeloma), lymphoma and amyloidosis.
- Other diseases. These include kidney disease, liver disease, connective tissue disorders and an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism).
- In a number of cases, no cause can be identified (idiopathic).
Symptoms
Every nerve in your peripheral system has a specific function, so symptoms depend on the type of nerves affected. Nerves are classified into:
- Sensory nerves that receive sensation, such as temperature, pain, vibration or touch, from the skin
- Motor Nerves that control muscle movement
- Autonomic Nerves that control functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, digestion and bladder
Signs and symptoms of peripheral neuropathy might include:
- Gradual onset of numbness, prickling or tingling in your feet or hands, which can spread upward into your legs and arms
- Sharp, jabbing, throbbing, freezing or burning pain
- Extreme sensitivity to touch
- Lack of coordination and falling
- Muscle weakness or paralysis if motor nerves are affected
If autonomic nerves are affected, signs and symptoms might include:
- Heat intolerance and altered sweating
- Bowel, bladder, or digestive problems
- Changes in blood pressure, causing dizziness or lightheadedness
Peripheral neuropathy can affect one nerve (mononeuropathy), two or more nerves in different areas (multiple mononeuropathy) or many nerves (polyneuropathy). Carpal tunnel syndrome is an example of mononeuropathy. Most people with peripheral neuropathy have polyneuropathy.
When to come see me?
Seek medical care right away if you notice unusual tingling, weakness, or pain in your hands or feet. Early diagnosis and treatment offer the best chance for controlling your symptoms and preventing further damage to your peripheral nerves.
Treatment
While pain medications can temporarily relieve neuropathy pain, they may also produce undesirable side effects or no results.
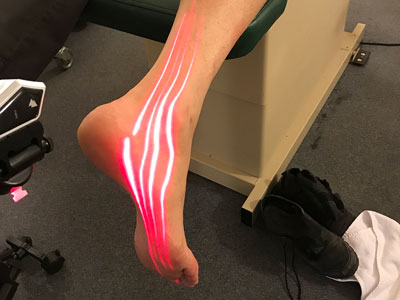
That’s why we are offering alternative therapies for opioid-free / drug fee for acute, and or chronic neuropathy pain or circulatory disorders symptoms patients.
One of the most effective non-surgical, drug-free treatments we offer is Electroanalgesia (EA) with the NeuroSanos software version 5/1.0 which is a FDA cleared medical device that has clinical indication of use to: 1) Stimulate peripheral nerves for the purpose of providing pain relief. 2) Increasing local blood circulation. 3) Management and symptomatic relief of chronic (Long-term) INTRACTABLE PAIN.
This treatment modality, often termed as "Physical Medicine Treatment” and “Electroanalgesia” (EA) therapy, utilizes the application of frequency .1 - .5 Hz (Physical Medicine Treatment) and 5,000 Hz, 8,300 Hz (Electroanalgesia) achieve a variety of therapeutic actions including reduction of edema, and inflammation, analgesia, and facilitation of metabolism in the neuropathic extremity.
Electroanalgesia (EA) is accomplished by placing special designed conductive sock or hand garment electrodes over the treatment area. The strength of EA treatment is to reduce the ability of the affected nerves to transmit pain signals and, at the same time, promote healing by means of the depolarization effects on the nerve cells.
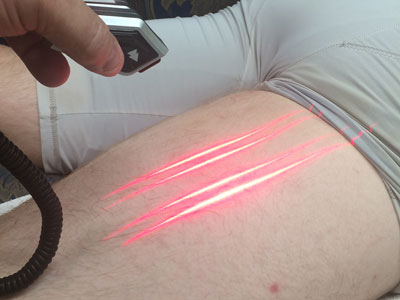
This medical device uses specific patented pre-programmed software algorithms to bioelectrically trigger different desired physiological mechanisms of actions from frequencies starting at .1 Hz - .5 Hz (for stimulation) then changing throughout the treatment to include a 5,000 Hz frequency. This technology also uses a High Definition frequency generator (HDfg)™ that can produce much higher frequencies, (8,300 Hz) to inhibit the nerves. EA technology is continually using a specific 1) carrier frequency, 2) and physician is changing the intensity (dosage) of the current to precisely match parameters delivered at the appropriate time.
Electroanalgesia are very successful. Results show that 75-80% of patients get better with treatment and have lasting results; however, there is no guarantee of success. Note that 20-25% of patients will claim they received little or no long-term relief. For this reason, other treatment options should be added or considered.
Before & After Treatment
Before Treatment